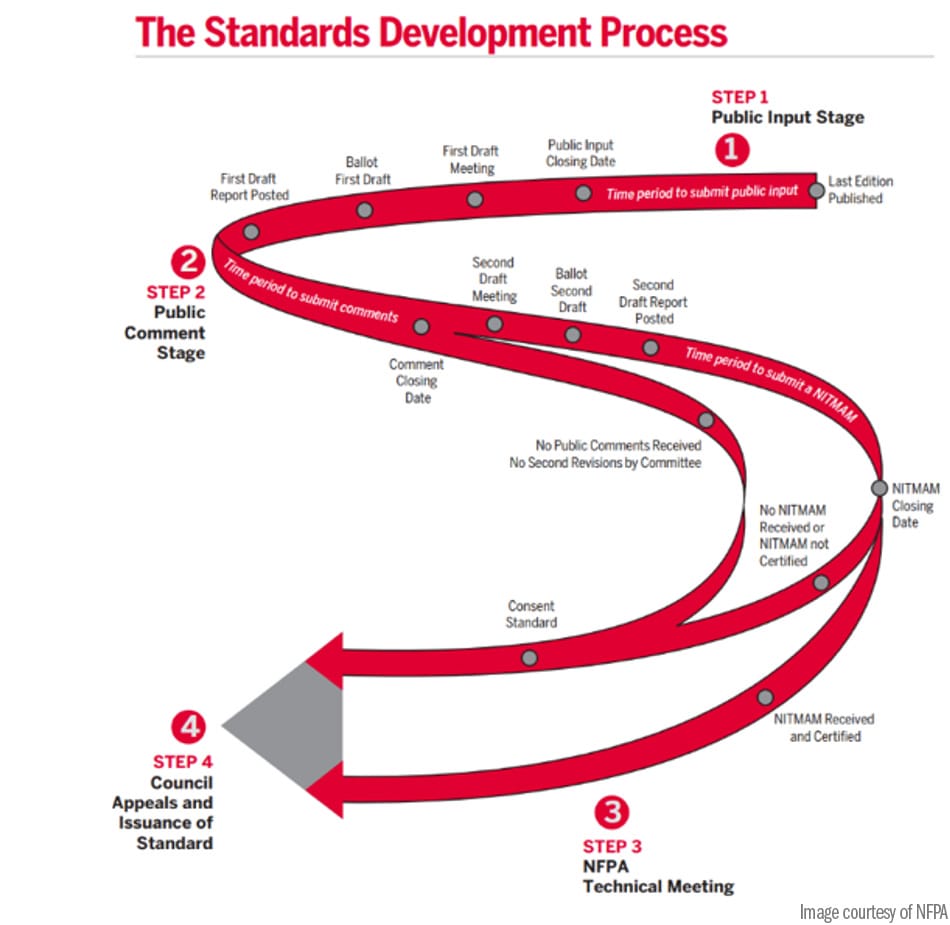
The Standards Development Process
Where do requirements come from, and how do they get there? We’ve all been there. You receive bid documents from an engineering firm, bid the project per the provided layout, win the job, and then complete shop drawings for plan review and permitting. Only to have them rejected. It turns out the local Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) adopted a new code edition, and the code has changed.
Have you ever wondered about the process that goes into changing the code? Recently, Nicole Hickman, an Engineering Manager from Midwest Alarm Services, traveled to Salt Lake City, UT, to attend and participate in the NFPA 72 First Draft Meeting. Here’s a basic rundown of what happened.
The diagram below illustrates this process.
Step 1: Public Input
Anyone can submit a Public Input to be considered for upcoming code editions. During this first step, a Technical Committee reviews all the submitted input at a First Draft meeting and provides responses. They then ballot the changes, which must have two-thirds support. Following the ballot, a First Draft Report is posted for Step 2.
Step 2: Public Comment Stage
Just like the song says, “Second verse, same as the first.” Anyone can review, object, or make additional suggestions on the First Draft. The Technical Committee then meets again for the Second Draft meeting, reviews the feedback, and posts the Second Draft Report after a ballot.
Step 3: NFPA Technical Meeting
From here, you get one more chance to advocate for your point during Step 3, the NFPA Technical Meeting. First, you need to file a motion. After that, you or a trusted friend or colleague needs to show up to the Tech Meeting, which immediately follows the annual NFPA Conference. You plead your case, anyone present has the opportunity to plead theirs, and then Registered Voting Members of NFPA vote on the outcome.
Step 4: Council Appeals and Issuance of Standard
Step 4 allows for a final appeal before they decide whether to issue the standard or take other action.
For a full rundown on the process, check out the official NFPA standards development page.
Major Changes in the 2025 Edition of NFPA 72
The 2025 edition of NFPA 72 introduces several significant updates that will affect fire alarm systems and installations. Some of the major changes include:
- Cybersecurity: Chapter 11 has been extensively expanded to protect fire alarm and signaling systems.
- Smoke Detector Spacing: The spacing remains unchanged for ceilings up to 40 feet; detection then moves to performance-based designs.
- Battery Requirements: Rechargeable batteries used for secondary power need to be listed by an approved agency. In case you missed it, the correction factor for battery aging was increased to 25% in the 2022 edition.
- Voltage Drop Calculations: Detailed instructions now clarify how to calculate different types of circuits.
- Restricted Audible Mode Operation (RAMO): This new notification mode can be used where a risk analysis has been performed, especially in areas where sudden loud noises would adversely affect the occupants. Similar to Private Mode, sound levels may be reduced where trained, awake, and mobile staff are present.
- Control Unit Diagrams: Don’t forget to start adding Control Unit Diagrams to your Shop Drawing Requirements. They should include identification, locations, and field wiring terminations.
- Record of Completion (ROC) Documentation: We all love ROC documentation. Clarification has been added on the responsibility for ROCs. Installing contractors must submit them to the AHJ and the Owner at closeout. When multiple contractors are involved, responsibility for your part of the project has been defined.
At Midwest Alarm Services, our team is committed to staying on top of these crucial code changes to ensure every project meets the highest standards for safety and compliance.